Ransomware cashouts down 35% as victims snub demand: Chainalysis
Ransomware attacks jumped last year, but victims’ payments decreased while users refused to respond to requests in a context of increased recovery efficiency by the police.
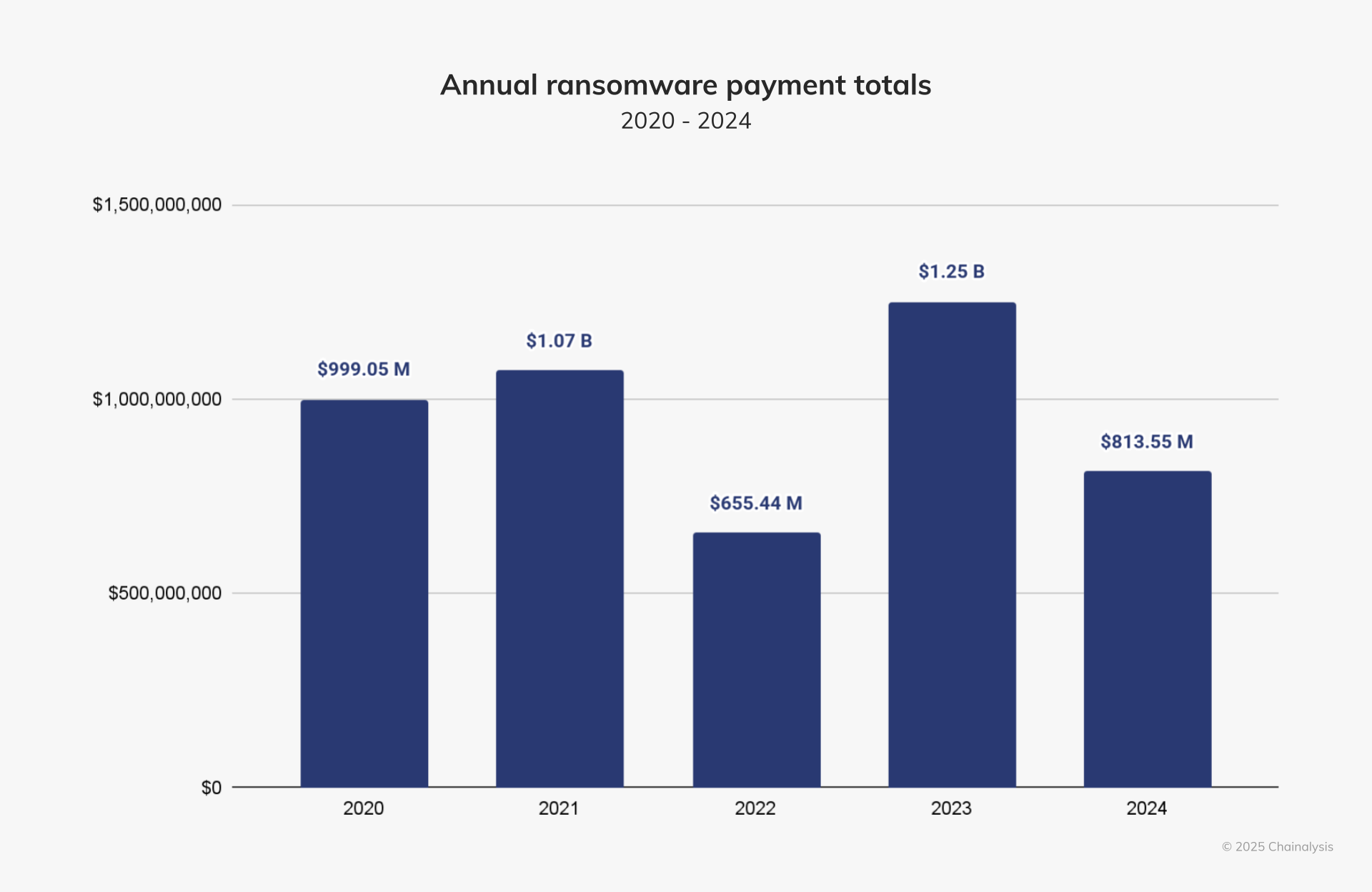
The lucrative activity of ransomware has gained less payments from victims from one year to the next despite an increase in attacks launched by bad players in 2024, according to a chain crime analysis report.
The report revealed that ransomware payments dropped by 35% last year, totaling $ 813 million against $ 1.25 billion in the previous year. Cybercriminals initially experienced success in the first half of 2024, with a 2.3% increase in successful extortion attempts, including $ 75 million collected by the illegal group of Dark Angels.
However, improving cryptographic survey practices, sanctions and asset seizures disrupted criminal networks during the second half of the year. The analysis chain noted that restrictions On the Russian EXCHANGE Crypto, Cryptx and Germany’s repression on 47 Russian platforms have considerably hampered ransomware money laundering operations.
Jacqueline Burns Koven, head of the cyber-menace of the intelligence chain, wrote that bad actors were increasingly hesitating to withdraw criminal products via centralized cryptography exchanges. However, CEX Non Kyc platforms have remained the favorite canal to convert the stolen crypto into a fiduciary currency.
More victims have also refused to pay ransoms despite the growing frequency of cyber attacks, encouraged by improving the layout of crypto and reinforced investigation efforts.
Less than 50% of ransomware campaigns gave payments in 2024. Those who complied generally paid up to $ 250,000 in ransom requests. However, the attackers adapted to the evolution of security measures, using new strategies to violate the databases and put pressure on the victims to pay.
In response, many attackers have changed tactics, with new ransomware strains emerging from a renowned, disclosed or purchased code, reflecting a more adaptive and agile threat environment. Ransomware operations have also become faster, negotiations often starting within hours of data exfiltration. The attackers range from the actors of the nation-state to ransomware operations as a service (RAAS), solitary operators and data flight extortion groups, such as those who have extorted and stolen from snowflake data, A cloud service provider.
Report on the crime of the channel chain 2025













Post Comment